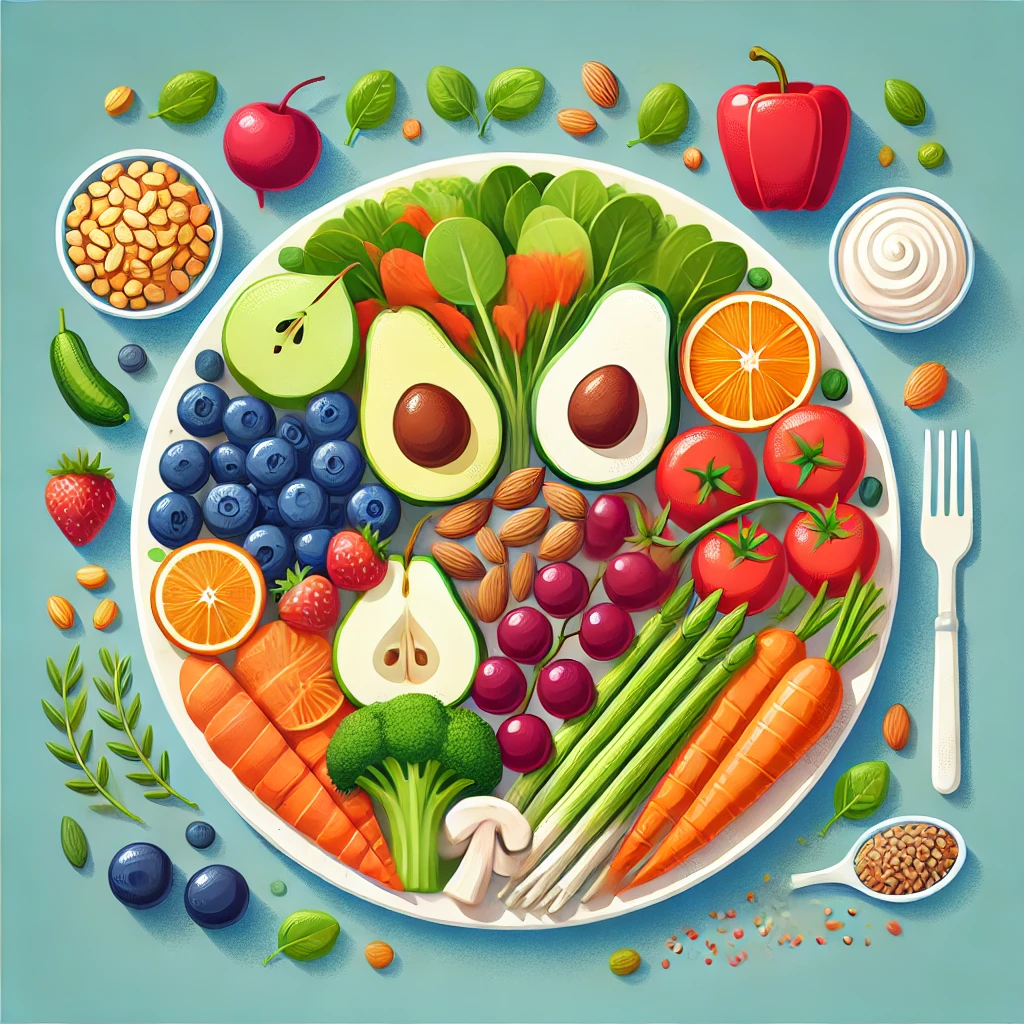
A balanced diet is the foundation of good health, promoting physical well-being, mental clarity, and energy. This guide will take you through every aspect of dieting, from A to Z, offering practical tips on how to maintain a healthy eating routine.
A – Antioxidants:
Antioxidants are compounds that help protect the body from free radicals, which can cause cell damage. Include foods rich in antioxidants like berries, nuts, and leafy greens to support immune function and fight aging.
B – Balanced diet:
A balanced diet includes a mix of macronutrients (carbs, proteins, fats) and micronutrients (vitamins, minerals). Ensure each meal contains vegetables, protein sources, and whole grains for optimal health.
1.Balanced diet: A Step Towards a Healthier You
A balanced diet is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. It includes the right proportions of carbohydrates, proteins, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals. Eating a variety of nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins helps boost immunity, improve digestion, and maintain energy levels. Staying hydrated and avoiding processed foods further enhances health. A well-balanced diet not only supports physical fitness but also improves mental clarity and emotional well-being. Prioritizing nutritious meals daily leads to a healthier and more fulfilling life.
2.Balanced diet: Nourish Your Body the Right Way
A balanced diet provides essential nutrients your body needs to function optimally. It includes a mix of proteins, carbohydrates, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals from whole foods like fruits, vegetables, grains, and lean proteins. Eating a variety of nutrient-rich foods boosts immunity, improves digestion, and maintains energy levels. Hydration and portion control are also key factors in a well-balanced diet. By making mindful food choices, you can support overall health, enhance metabolism, and lead a more active lifestyle.
C – Carbohydrates:
Carbs provide energy to the body. Opt for complex carbs like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables instead of refined sugars and white bread to avoid blood sugar spikes.
D – Dietary fiber:
Fiber helps with digestion and maintaining a healthy weight. Foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are rich in fiber. Aim for at least 25 grams of fiber daily.
E – Eating habits: Balance diet.
Good eating habits include eating slowly, portion control, and listening to your body’s hunger cues. Avoid skipping meals and aim for smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day.
F – Fats:
Healthy fats, found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, support brain function, skin health, and hormone regulation. Limit saturated and trans fats to protect heart health.
G – Green vegetables: Balance diet.
Green vegetables like spinach, broccoli, and kale are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. They help boost immunity and support digestive health.
H – Hydration:
Drinking enough water is essential for overall health. Water aids digestion, regulates body temperature, and helps flush toxins. Aim for 8-10 glasses a day, or more if you’re active.
I – Intermittent fasting:
Intermittent fasting is a dietary approach that cycles between periods of eating and fasting. It may help with weight management and improve metabolic health when done properly.
J – Juices:
Fresh fruit and vegetable juices can be a great addition to your diet. However, avoid sugary store-bought juices. Opt for homemade, nutrient-packed juices to maximize health benefits.
K – Keto diet:
The ketogenic (keto) diet is a low-carb, high-fat eating plan that can promote weight loss and improve brain function. It’s important to consult a doctor before starting the keto diet.
L – Lean proteins:
Lean proteins such as chicken, turkey, tofu, and fish are low in fat and help build and repair tissues. Including adequate protein helps in muscle maintenance and weight management.
M – Micronutrients:
Vitamins and minerals, though needed in smaller amounts, are vital for proper body function. Ensure you include a variety of fruits and vegetables to meet your micronutrient needs.
N – Nutrient-dense foods:
Nutrient-dense foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Examples include leafy greens, berries, nuts, and fish. Focus on nutrient-dense foods to ensure you’re getting the most from your meals.
O – Organic foods:
Organic foods are grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers. While they may be more expensive, they may offer greater nutritional benefits and fewer chemicals in your diet.
P – Portion control:
Portion control is essential for maintaining a healthy weight. Pay attention to portion sizes, and avoid overeating by listening to your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
Q – Quinoa:
Quinoa is a nutrient-rich grain that is a great source of protein, fiber, and essential amino acids. It’s a versatile addition to salads, bowls, and as a side dish.
R – Raw foods:
Raw foods, like fruits, vegetables, and nuts, are rich in enzymes and nutrients. Incorporating raw food into your diet can help maintain optimal health and energy levels.
S – Supplements:
Supplements can help fill any gaps in your diet, particularly if you have specific nutrient deficiencies. However, it’s best to get most of your nutrients from whole foods.
T – Timing:
Meal timing is important for maintaining energy levels throughout the day. Try to eat within 1-2 hours of waking up, and avoid large meals right before bedtime.
U – Unprocessed foods:
Unprocessed foods, such as whole grains, lean meats, and fresh fruits, contain fewer additives and preservatives. Choose whole, natural foods for a healthier diet.
V – Vegetables:
Vegetables are essential for a balanced diet and should make up a large part of your meals. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants.
W – Whole grains:
Whole grains like brown rice, oats, and whole wheat bread are rich in fiber and provide long-lasting energy. They help regulate blood sugar and support digestive health.
X – Xenobiotics:
Xenobiotics are foreign substances found in food, such as pesticides or chemicals used in processing. Minimize exposure by choosing organic and non-processed foods when possible.
Y – Yogurt:
Yogurt is a great source of probiotics, which promote gut health. It can improve digestion and boost the immune system, but opt for plain, unsweetened varieties.
Z – Zinc:
Zinc is an essential mineral that supports immune function, wound healing, and protein synthesis. Foods rich in zinc include meat, shellfish, seeds, and legumes.
Conclusion:
A balanced diet is essential to maintaining health and preventing chronic diseases. By incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods and focusing on portion control, hydration, and mindful eating, you can achieve your health goals and feel your best.https://india24hrs.com/understanding-diabetes-in-2024-a-comprehensive-guide-for-health-and-wellness/